Information Model on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An information model in
An information model in
"Information modeling from design to implementation"
National Institute of Standards and Technology.

 In 1976, an entity-relationship (ER) graphic notation was introduced by
In 1976, an entity-relationship (ER) graphic notation was introduced by
- the Eiffel tower Paris
- Paris city
whereas information requirements and knowledge can be expressed for example as follows:
- tower geographical area
- city geographical area
Such Gellish expressions use names of concepts (such as 'city') and relation types (such as and ) that should be selected from the Gellish Formal English Dictionary-Taxonomy (or of your own domain dictionary). The Gellish English Dictionary-Taxonomy enables the creation of semantically rich information models, because the dictionary contains definitions of more than 40000 concepts, including more than 600 standard relation types. Thus, an information model in Gellish consists of a collection of Gellish expressions that use those phrases and dictionary concepts to express facts or make statements, queries and answers.
Gellish, A Generic Extensible Ontological Language
(PhD, Delft University of Technology, 2005) *
 An information model in
An information model in software engineering
Software engineering is a systematic engineering approach to software development.
A software engineer is a person who applies the principles of software engineering to design, develop, maintain, test, and evaluate computer software. The term '' ...
is a representation of concepts and the relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. Typically it specifies relations between kinds of things, but may also include relations with individual things. It can provide sharable, stable, and organized structure of information requirements or knowledge for the domain context.Y. Tina Lee (1999)"Information modeling from design to implementation"
National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Overview
The term ''information model'' in general is used for models of individual things, such as facilities, buildings, process plants, etc. In those cases, the concept is specialised to facility information model,building information model
Building information modeling (BIM) is a process supported by various tools, technologies and contracts involving the generation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. Building informatio ...
, plant information model, etc. Such an information model is an integration of a model of the facility with the data and documents about the facility.
Within the field of software engineering and data modeling
Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques.
Overview
Data modeling is a process used to define and analyze data requirements needed to suppo ...
, an information model is usually an abstract, formal representation of entity types that may include their properties, relationships and the operations that can be performed on them. The entity types in the model may be kinds of real-world objects, such as devices in a network, or occurrences, or they may themselves be abstract, such as for the entities used in a billing system. Typically, they are used to model a constrained domain that can be described by a closed set of entity types, properties, relationships and operations.
An information model provides formalism to the description of a problem domain without constraining how that description is mapped to an actual implementation in software. There may be many mappings of the information model. Such mappings are called data model
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be co ...
s, irrespective of whether they are object model
In computing, object model has two related but distinct meanings:
# The properties of objects in general in a specific computer programming language, technology, notation or methodology that uses them. Examples are the object models of ''Java'', ...
s (e.g. using UML
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The creation of UML was originally m ...
), entity relationship models or XML schema
An XML schema is a description of a type of Extensible Markup Language, XML document, typically expressed in terms of constraints on the structure and content of documents of that type, above and beyond the basic syntactical constraints imposed ...
s.
Information modeling languages
Peter Chen
Peter Pin-Shan Chen (; born 3 January 1947) is a Taiwanese American computer scientist. He is a (retired) distinguished career scientist and faculty member at Carnegie Mellon University and Distinguished Chair Professor Emeritus at LSU. He is ...
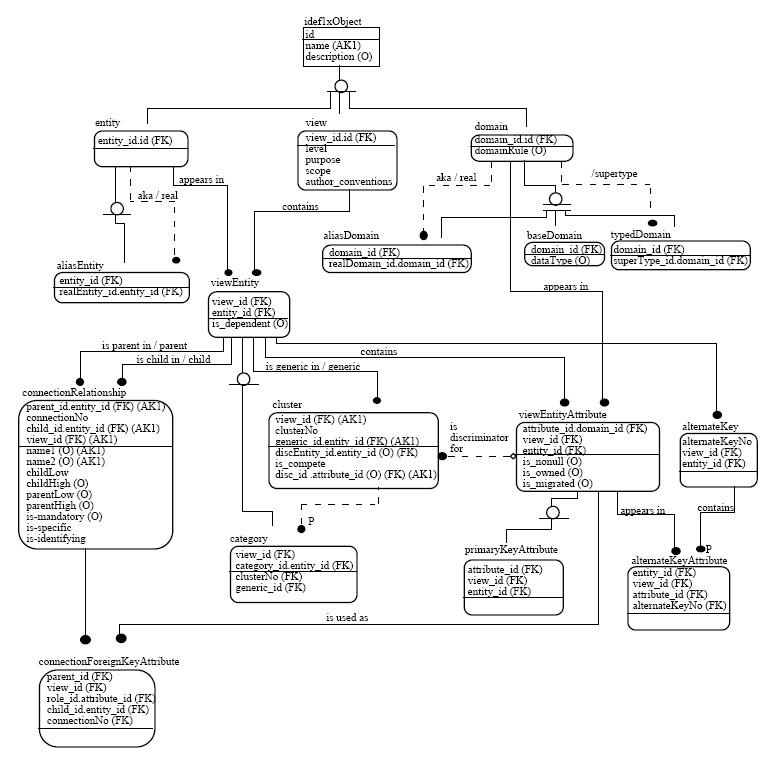
. He stressed that it was a "semantic" modelling technique and independent of any database modelling techniques such as Hierarchical, CODASYL, Relational etc. Since then, languages for information models have continued to evolve. Some examples are the Integrated Definition Language 1 Extended (IDEF1X
Integration DEFinition for information modeling (IDEF1X) is a data modeling language for the development of semantic data models. IDEF1X is used to produce a graphical information model which represents the structure and semantics of information ...
), the EXPRESS
Express or EXPRESS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Express: Aisle to Glory'', a 1998 comedy short film featuring Kal Penn
* '' The Express: The Ernie Davis Story'', a 2008 film starring Dennis Quaid
Music
* ''Express'' ...
language and the Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The creation of UML was originally m ...
(UML).
Research by contemporaries of Peter Chen such as J.R.Abrial (1974) and G.M Nijssen (1976) led to today's Fact Oriented Modeling (FOM) languages which are based on linguistic propositions rather than on "entities". FOM tools can be used to generate an ER model which means that the modeler can avoid the time-consuming and error prone practice of manual normalization. Object-Role Modeling language (ORM
Orm (in Old Norse and in modern Danish, Swedish, Norwegian (bokmål and nynorsk) the word for "snake", "worm" or "dragon") became an Anglo-Saxon personal name during period of the Danelaw.
Orm may also refer to:
* Orm or Ormin, the author of ...
) and Fully Communication Oriented Information Modeling (FCO-IM
Fully Communication Oriented Information Modeling (FCO-IM) is a method for building conceptual information models. Such models can then be automatically transformed into entity-relationship models (ERM), Unified Modeling Language (UML), relation ...
) are both research results, based upon earlier research.
In the 1980s there were several approaches to extend Chen’s Entity Relationship Model. Also important in this decade is REMORA by Colette Rolland
Colette Rolland (born 1943, in Dieupentale, Tarn-et-Garonne, France) is a French computer scientist and Professor of Computer Science in the department of Mathematics and Informatics at the University of Paris 1 Pantheon-Sorbonne, and a leading ...
.
The ICAM Definition (IDEF) Language was developed from the U.S. Air Force ICAM Program during the 1976 to 1982 timeframe. The objective of the ICAM Program, according to Lee (1999), was to increase manufacturing productivity through the systematic application of computer technology. IDEF includes three different modeling methods: IDEF0
IDEF0, a compound acronym ("Icam DEFinition for Function Modeling", where ICAM is an acronym for "Integrated Computer Aided Manufacturing"), is a function modeling methodology for describing manufacturing functions, which offers a functional modeli ...
, IDEF1
Integration DEFinition for information modeling (IDEF1X) is a data modeling language for the development of semantic data models. IDEF1X is used to produce a graphical information model which represents the structure and semantics of information ...
, and IDEF2
IDEF, initially an abbreviation of ICAM Definition and renamed in 1999 as Integration Definition,IEEE Standard for Functional Modeling Language—Syntax and Semantics for IDEF0, Software Engineering Standards Committee of the IEEE Computer Soci ...
for producing a functional model, an information model, and a dynamic model respectively. IDEF1X
Integration DEFinition for information modeling (IDEF1X) is a data modeling language for the development of semantic data models. IDEF1X is used to produce a graphical information model which represents the structure and semantics of information ...
is an extended version of IDEF1. The language is in the public domain. It is a graphical representation and is designed using the ER approach and the relational theory. It is used to represent the “real world” in terms of entities, attributes, and relationships between entities. Normalization is enforced by KEY Structures and KEY Migration. The language identifies property groupings (Aggregation) to form complete entity definitions.
EXPRESS
Express or EXPRESS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Express: Aisle to Glory'', a 1998 comedy short film featuring Kal Penn
* '' The Express: The Ernie Davis Story'', a 2008 film starring Dennis Quaid
Music
* ''Express'' ...
was created as ISO 10303-11 for formally specifying information requirements of product data model. It is part of a suite of standards informally known as the STandard for the Exchange of Product model data (STEP). It was first introduced in the early 1990s.D. Schenck and P. Wilson (1994). ''Information Modeling the EXPRESS Way.'' Oxford University Press, New York, NY, 1994. The language, according to Lee (1999), is a textual representation. In addition, a graphical subset of EXPRESS called EXPRESS-G is available. EXPRESS is based on programming languages and the O-O paradigm. A number of languages have contributed to EXPRESS. In particular, Ada, Algol, C, C++, Euler, Modula-2, Pascal, PL/1, and SQL. EXPRESS consists of language elements that allow an unambiguous object definition and specification of constraints on the objects defined. It uses SCHEMA declaration to provide partitioning and it supports specification of data properties, constraints, and operations.
UML is a modeling language for specifying, visualizing, constructing, and documenting the artifacts, rather than processes, of software systems. It was conceived originally by Grady Booch
Grady Booch (born February 27, 1955) is an American software engineer, best known for developing the Unified Modeling Language (UML) with Ivar Jacobson and James Rumbaugh. He is recognized internationally for his innovative work in software archit ...
, James Rumbaugh
James E. Rumbaugh (born August 22, 1947) is an American computer scientist and object-oriented methodologistIvar Jacobson
Ivar Hjalmar Jacobson (born 1939) is a Swedish computer scientist and software engineer, known as major contributor to UML, Objectory, Rational Unified Process (RUP), aspect-oriented software development and Essence.
Biography
Ivar Jacobson w ...
. UML was approved by the Object Management Group
The Object Management Group (OMG) is a computer industry standardization, standards consortium. OMG Task Forces develop enterprise integration standards for a range of technologies.
Business activities
The goal of the OMG was a common portabl ...
(OMG) as a standard in 1997. The language, according to Lee (1999), is non-proprietary and is available to the public. It is a graphical representation. The language is based on the objected-oriented paradigm. UML contains notations and rules and is designed to represent data requirements in terms of O-O diagrams. UML organizes a model in a number of views that present different aspects of a system. The contents of a view are described in diagrams that are graphs with model elements. A diagram contains model elements that represent common O-O concepts such as classes, objects, messages, and relationships among these concepts.
IDEF1X, EXPRESS, and UML all can be used to create a conceptual model and, according to Lee (1999), each has its own characteristics. Although some may lead to a natural usage (e.g., implementation), one is not necessarily better than another. In practice, it may require more than one language to develop all information models when an application is complex. In fact, the modeling practice is often more important than the language chosen.
Information models can also be expressed in formalized natural languages, such as Gellish
Gellish is an ontology language for data storage and communication, designed and developed by Andries van Renssen since mid-1990s. It started out as an engineering modeling language ("Generic Engineering Language", giving it the name, "Gellish") bu ...
. Gellish, which has natural language variants Gellish Formal English, Gellish Formal Dutch (Gellish Formeel Nederlands), etc. is an information representation language or modeling language that is defined in the Gellish smart Dictionary-Taxonomy, which has the form of a Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
/Ontology
In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, becoming, and reality.
Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into categories and which of these entities exis ...
. A Gellish Database is not only suitable to store information models, but also knowledge models, requirements models and dictionaries, taxonomies and ontologies. Information models in Gellish English use Gellish Formal English expressions. For example, a geographic information model might consist of a number of Gellish Formal English expressions, such as: - the Eiffel tower
Standard sets of information models
TheDistributed Management Task Force
Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) is a 501(c)(6) nonprofit industry standards organization that creates open manageability standards spanning diverse emerging and traditional IT infrastructures including cloud, virtualization, network, s ...
(DMTF) provides a standard set of information models for various enterprise domains under the general title of the Common Information Model (CIM). Specific information models are derived from CIM for particular management domains.
The TeleManagement Forum
TM Forum is a global industry association for service providers and their suppliers in the telecommunications industry. Members include communications and digital service providers, telephone companies, cable operators, network operators, cloud ...
(TMF) has defined an advanced model for the Telecommunication domain (the Shared Information/Data model, or SID) as another. This includes views from the business, service and resource domains within the Telecommunication industry. The TMF has established a set of principles that an OSS integration should adopt, along with a set of models that provide standardized approaches.
The models interact with the information model (the Shared Information/Data Model, or SID), via a process model
The term process model is used in various contexts. For example, in business process modeling the enterprise process model is often referred to as the ''business process model''.
Overview
Process models are processes of the same nature that ar ...
(the Business Process Framework (eTOM), or eTOM) and a life cycle model.
See also
*Building information modeling
Building information modeling (BIM) is a process supported by various tools, technologies and contracts involving the generation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. Building informatio ...
* Concept map
A concept map or conceptual diagram is a diagram that depicts suggested relationships between concepts. Concept maps may be used by instructional designers, engineers, technical writers, and others to organize and structure knowledge.
A conce ...
* Conceptual model (computer science)
Conceptual may refer to:
Philosophy and Humanities
*Concept
*Conceptualism
*Philosophical analysis (Conceptual analysis)
*Theoretical definition (Conceptual definition)
*Thinking about Consciousness (Conceptual dualism)
*Pragmatism (Conceptual pr ...
* System information modelling System information modelling (SIM) is the process of modelling complex connected systems. System information models are digital representations of connected systems, such as electrical instrumentation and control, power, and communication systems. ...
Notes
References
* ISO/IEC TR9007 Conceptual Schema, 1986 * Andries van RenssenGellish, A Generic Extensible Ontological Language
(PhD, Delft University of Technology, 2005) *
Further reading
*Richard Veryard
Richard Veryard FRSA (born 1955) is a British computer scientist, author and business consultant, known for his work on service-oriented architecture and the service-based business.
Biography
Veryard attended Sevenoaks School from 1966 to 1972, ...
(1992). ''Information modelling : practical guidance''. New York : Prentice Hall.
*
*
External links
* – Terminology for Policy-Based Management {{DEFAULTSORT:Information Model Data modeling Information technology management